北理工在甘草三萜化合物的酵母合成領(lǐng)域取得重要進(jìn)展
發(fā)布日期:2017-12-14 供稿:化學(xué)與化工學(xué)院朱明、馮旭東 攝影:李春課題組
編輯:秦月 審核:趙文祥 閱讀次數(shù):在國家杰出青年科學(xué)基金和國自然重點(diǎn)基金項(xiàng)目的資助下,北京理工大學(xué)化學(xué)與化工學(xué)院李春教授課題組在合成生物學(xué)與生物工程領(lǐng)域國際頂級期刊《Metabolic Engineering》發(fā)表文章:Boosting 11-oxo-β-amyrin and glycyrrhetinic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via pairing novel oxidation and reduction system from legume plants( Metab Eng. 2018, 45: 43-50,IF="8.142)。
萜烯類化合物是植物天然產(chǎn)物中最大的一類次級代謝產(chǎn)物,在抗炎癥、抗菌及癌細(xì)胞防治方面具有良好的藥物活性,甘草次酸作為重要的植物甘草中的三萜類化合物還具有保肝護(hù)肝與廣譜的病毒抑制等功效,但因其在植物中含量低和結(jié)構(gòu)復(fù)雜等因素限制了其廣泛應(yīng)用和化學(xué)全合成研究。李春教授課題組通過菌株篩選、氧化酶表征與植物基因轉(zhuǎn)錄組篩選新的CYP450氧化酶與CPR還原酶,并將氧化系統(tǒng)與還原系統(tǒng)重構(gòu)匹配耦合實(shí)現(xiàn)了電子的高效傳遞與應(yīng)用(圖1),并通過發(fā)酵工藝調(diào)控與優(yōu)化,創(chuàng)造性地實(shí)現(xiàn)并大幅度提高了釀酒酵母合成甘草次酸與11-氧-β-香樹脂醇的能力,為三萜類天然產(chǎn)物的人工生物合成奠定了重要基礎(chǔ),也為在酵母中進(jìn)行外源途徑的優(yōu)化和調(diào)控提供了新方法。
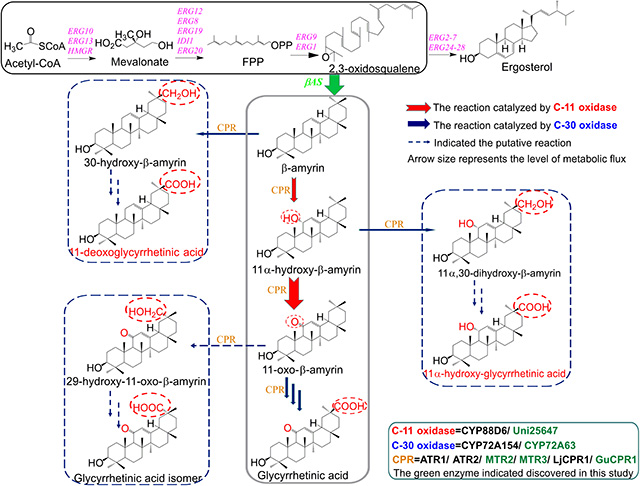
圖1 釀酒酵母中甘草次酸及其衍生物的合成路線設(shè)計(jì)
生物轉(zhuǎn)化與合成生物系統(tǒng)研究團(tuán)隊(duì)自2005年在北理工成立以來,專注于抗逆生物催化和合成生物學(xué)的研究,已在Metab Eng、Curr Opin Biotech、AIChE J、Chem Eng Sci、Chem Eng J、ACS Synth Biol、Nucleic Acids Res、Ind Eng Chem Res和Bioresource Technol等生物工程與化學(xué)工程領(lǐng)域的頂級期刊上發(fā)表文章120余篇,獲授權(quán)發(fā)明專利21項(xiàng)。課題組致力于利用合成生物技術(shù)和酶催化技術(shù)革新傳統(tǒng)微生物發(fā)酵與生物轉(zhuǎn)化模式,將繼續(xù)開展天然產(chǎn)物合成途徑的構(gòu)建、路徑的優(yōu)化與精確調(diào)控和生物過程集成的研究,為實(shí)現(xiàn)綠色、高效的藥物、生物基化學(xué)品的生物制造提供新思路和新方法
Professor Chun Li’s research group at School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology has made important progress in triterpenoid biosynthesis and related work has been published in Metabolic Engineering, ‘‘Boosting 11-oxo-β-amyrin and glycyrrhetinic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae via pairing novel oxidation and reduction system from legume plants’’( Metab Eng. 2018, 45: 43-50,IF="8.142)." This work is supported by the Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of China and the State Key Program of Natural Science Foundation of China.
Terpenoids are wide spread in plant with potential application in pharmaceutical activity, such as anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and cancer treatment. Glycyrrhetinic acid as an important triterpenoid mainly extracted from licorice root, exhibiting specific activities in hepatoprotective and broad-spectrum virus inhibition. But the low content in licorice and inefficient extraction process have limited its wide application. To solve this problem, Li group developed a novel and highly efficient pathway for the synthesis of glycyrrhetinic acid and 11-oxo-β-amyrin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by introducing efficient cytochrome P450s and pairing their reduction systems from legume plants through transcriptome and genome-wide screening and identification. The titer of glycyrrhetinic acid and 11-oxo-β-amyrin were further greatly improved through the fermentation process optimization. This study demonstrated the importance of pairing CYP450s and CPR for triterpenoids production. Moreover, this study is also helpful for constructing yeast cell factories for synthesizing other valuable triterpenoids.
分享到:
